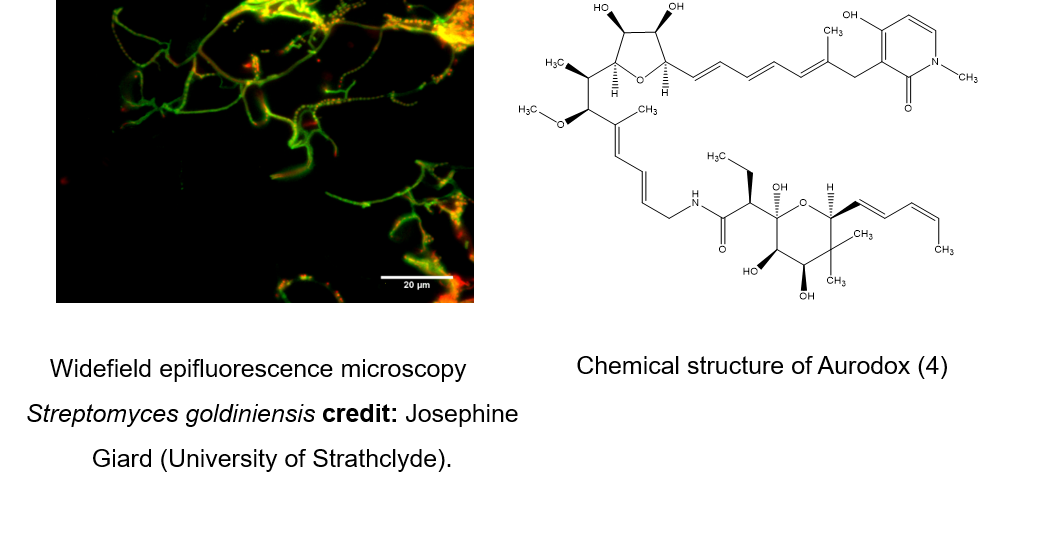
Streptomyces goldiniensis
From ActinoBase
Streptomyces goldiniensisis a Gram-positive soil dwelling bacterium that was first isolated from the island of Bermuda in 1969 (1). It produces Aurodox which has been shown to inhibit bacterial growth through binding to Elongation Factor Thermo-Unstable (Ef-Tu) (2), and has also been shown to transcriptionally inhibit Type III Secretion in Escherichia coli (3)
References
- Berger J, Lehr H, Teitel S, Maehr H, Grunberg E. 1973. A new antibiotic X-5108 OF Streptomyces origin. I. Production, isolation and properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 26:15–22.
- Vogeley L, Palm GJ, Mesters JR, Hilgenfeld R. 2001. Conformational change of elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) induced by antibiotic binding. Crystal structure of the complex between EF-Tu GDP and aurodox. J Biol Chem 276:17149–17155.
- McHugh RE, O’Boyle N, Connolly JPR, Hoskisson PA, Roe AJ. 2018. Characterisation of the mode of action of Aurodox, a Type III Secretion System inhibitor from Streptomyces goldiniensis. Infect Immun.
- Maehr H, Leach M, Yarmchuk L, Mitrovic M. 1979. Antibiotic X-5108. IX. Chemical conversion of mocimycin to aurodox and derivatives of aurodox, goldinamine and mocimycin. J Antibiot 32:361–367.